Distributed Systems
When faced with testing scenarios involve with either relative motion between components of interest or large physical dimensions, distributed measurement systems offer a way to accomplish the measurement task. In these situations, a cluster of small battery powered devices can offer the most efficient solution.
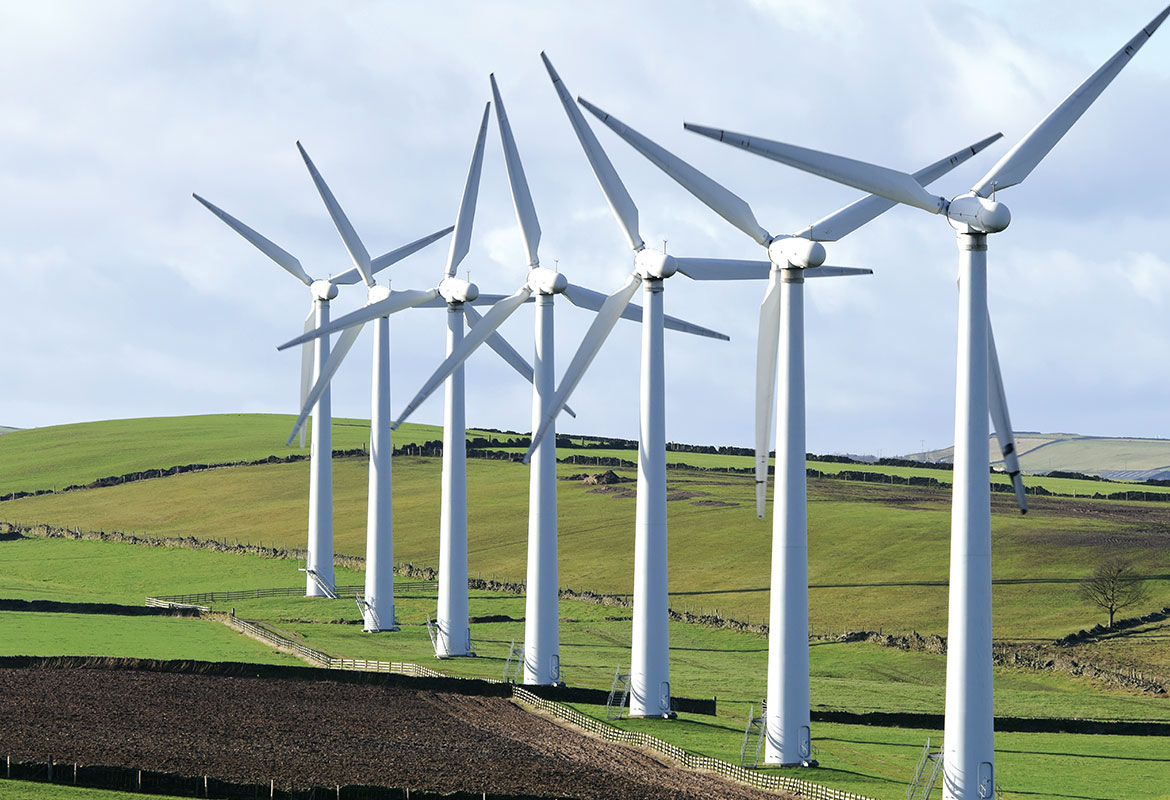
A wind turbine demonstrates both testing scenarios. Combining strain measurements on the turbine blades with stresses in the gearbox calls for relative motion testing, while testing the noise generated by the turbine will require you to measure large areas. Another interesting example is the use case of wide area beaming forming for the analysis of passenger jet fly-overs. These systems can have diameters on the order of 140 m with over 400 microphones.
To handle the physical and data rate implications of a system like this, it is wise to consider multiple acquisition units synchronized using either fiber optic VME synchronization or a one-wire solution of IEEE 1588-2008 (PTP) with PoE providing both synchronization and power with a single cable.
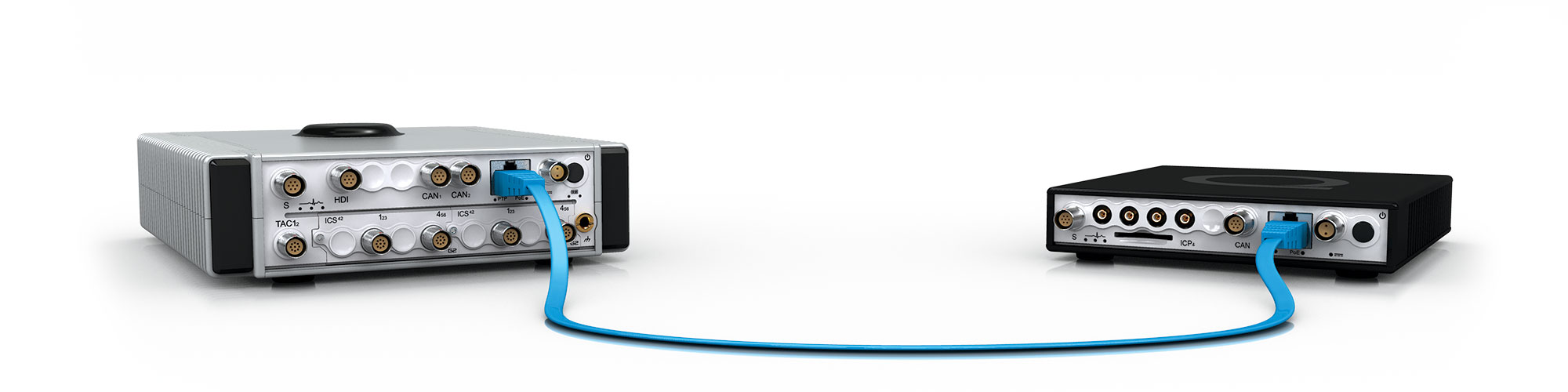

The MICROQ’s compact form
factor, built-in channels, capacity for extra measurement
channels and ability to synchronize via PTP or GPS makes it the
ideal solution.
MICROQ – battery powered,
built-in GPS and Wi-Fi
WSB42X – strain with constant voltage and constant
current
ICS42 – 6 ICP® / Voltage inputs tri-axial
connector
THM42 – 8 temperature / voltage / current inputs
Hardware to consider:
Ask about
our systems for higher channel counts, which contain PoE as well
as IEEE 1588-2008 PTP synchronization.
MIC42X – High dynamic range non-polarized microphone channels
PTP synchronization
Precision Time Protocol (PTP) is an IEEE 1588-2008 standard with high precision, accuracy and robustness using Ethernet as the communications medium.


GPS synchronization
GPS provides timing and precision data. This option allows any number of MICROQs to conveniently form a larger system through GPS synchronization. Users may choose to connect their MICROQs over built-in Wi-Fi (or Power over Ethernet) to a workstation.